Fresnel Zones
We want to take a more general look at diffraction by exploring a concept known as Fresnel zones. Consider spherical waves of wavelength
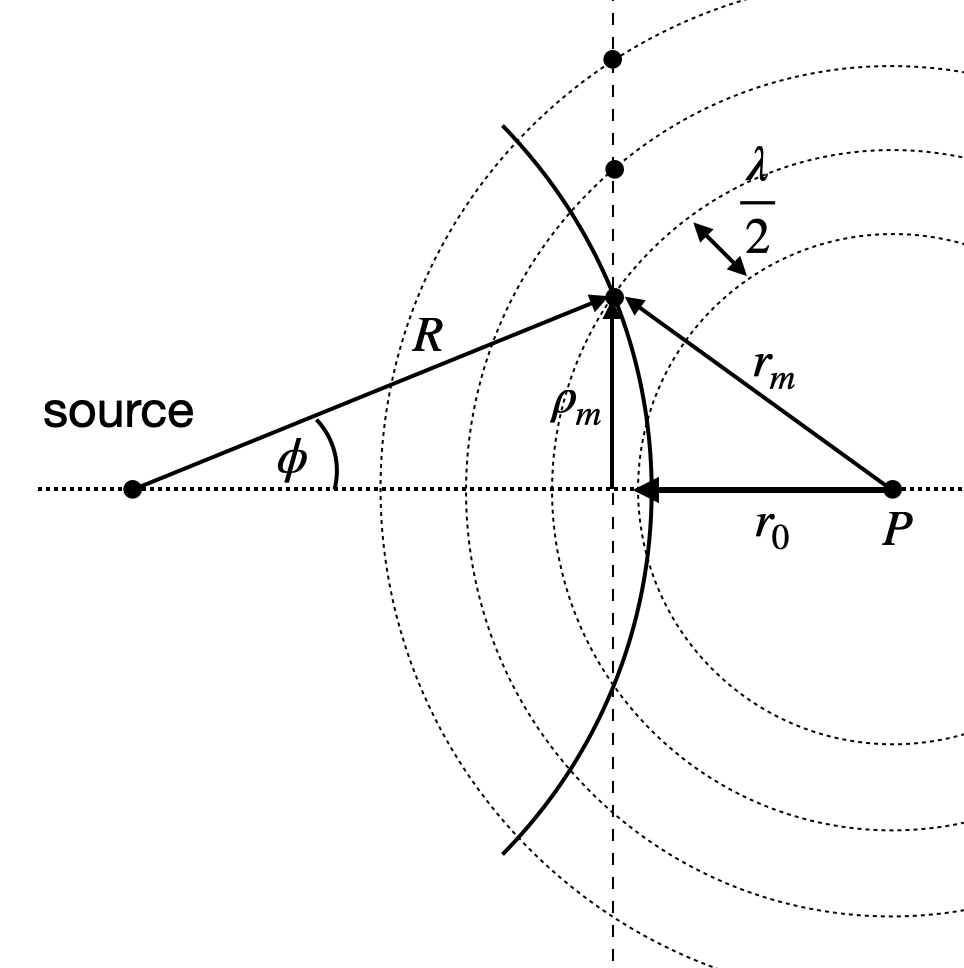
We will examine the intensity of the wave at a point
Instead of calculating the intensity explicitly, we will analyze the distances of individual points on the wavefront from point
where
according to the sketch above. This yields
For
which gives the radius of the individual zones. The width of the zones is given by
Fresnel Zone Plate
If we now fill the ring from
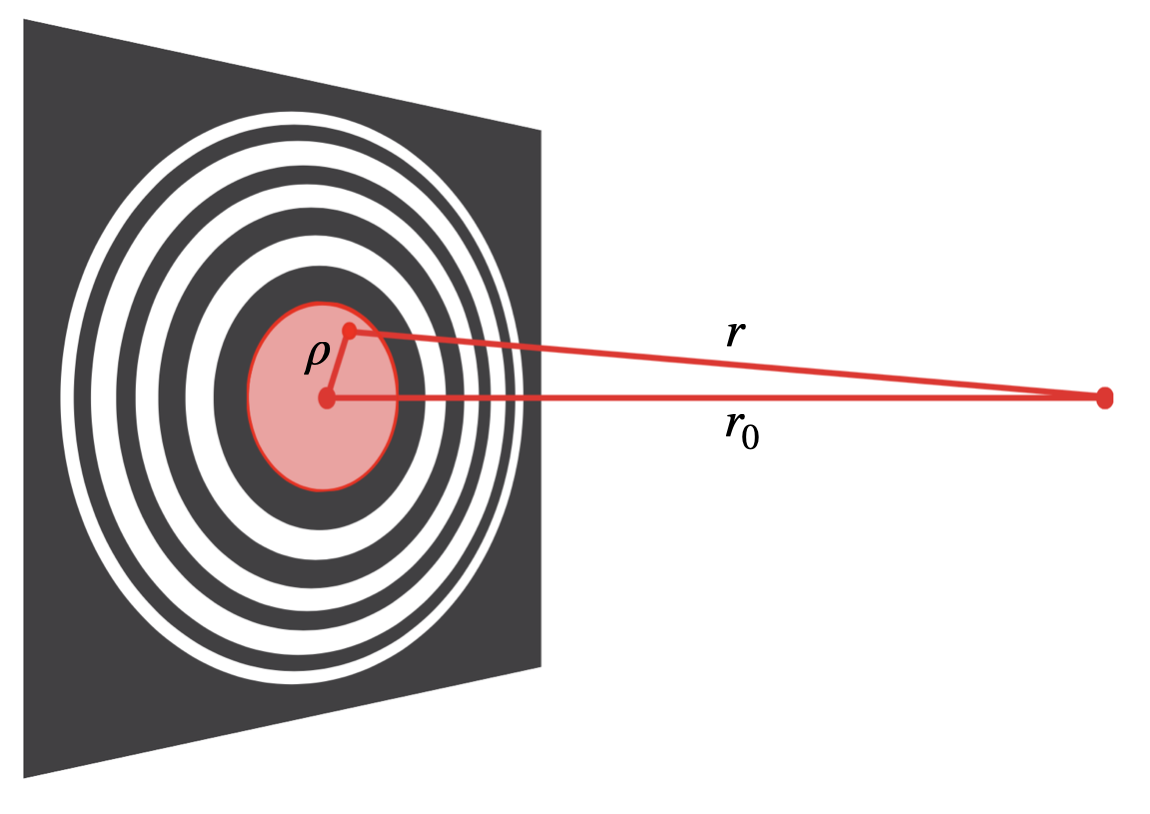
The Fresnel zone plate can be constructed by defining the inner reference zone in an arbitrary way. One may either block or transmit the direct path from the light source along the optical axis, resulting in either the odd or even zones being transparent.
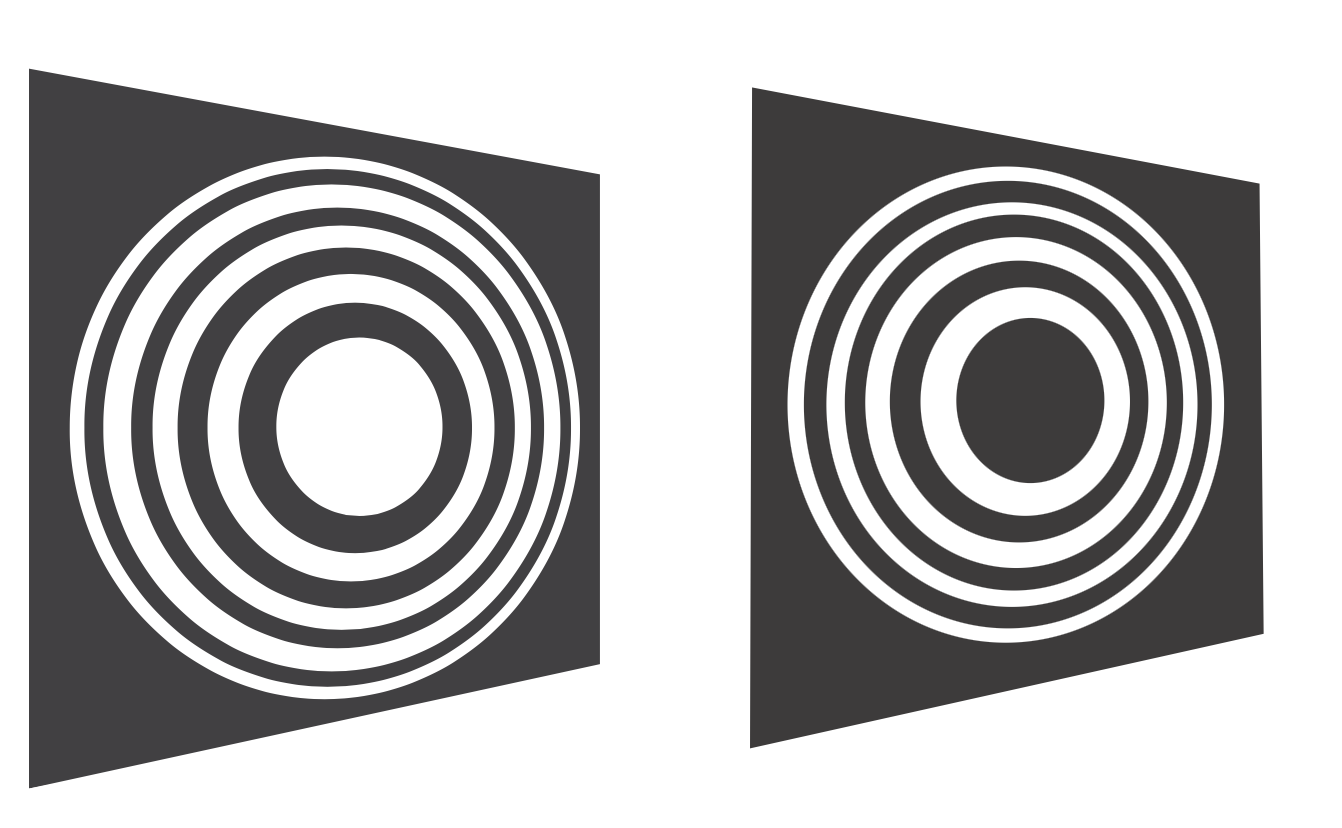

Such zone plates are important for applications where focusing of radiation is required but the refractive indices are not large enough to create strong enough refraction. This is especially true for X-ray radiation.
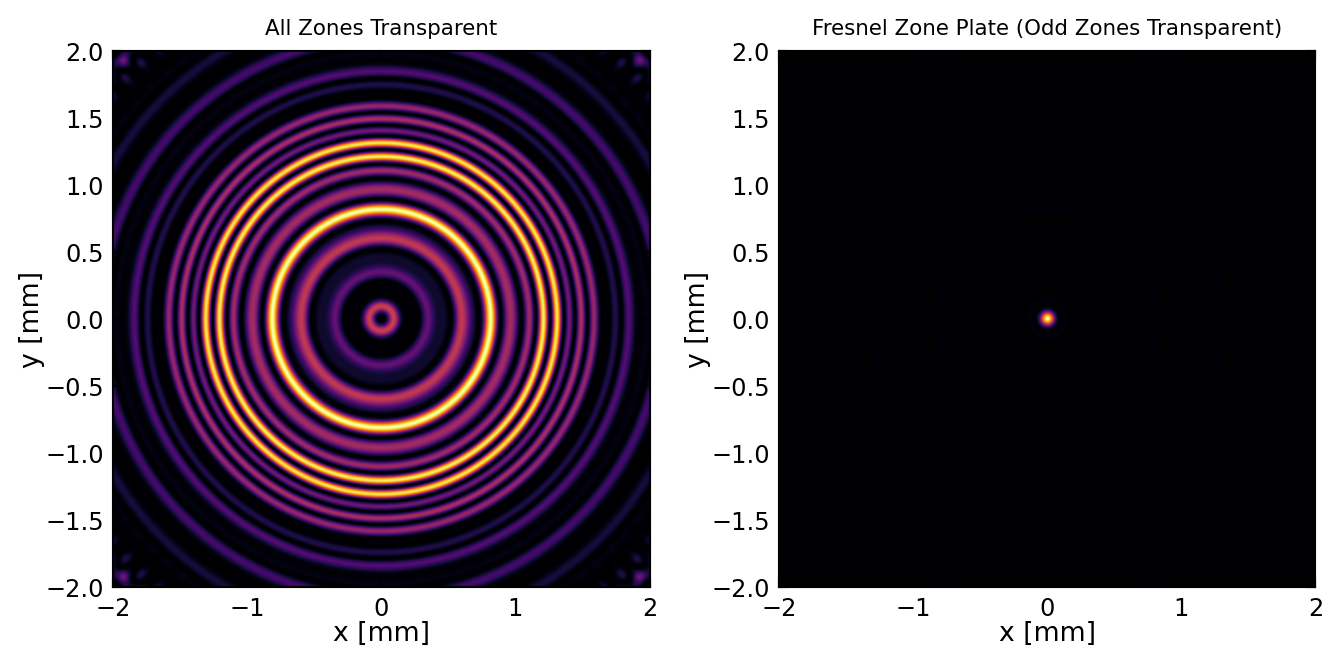
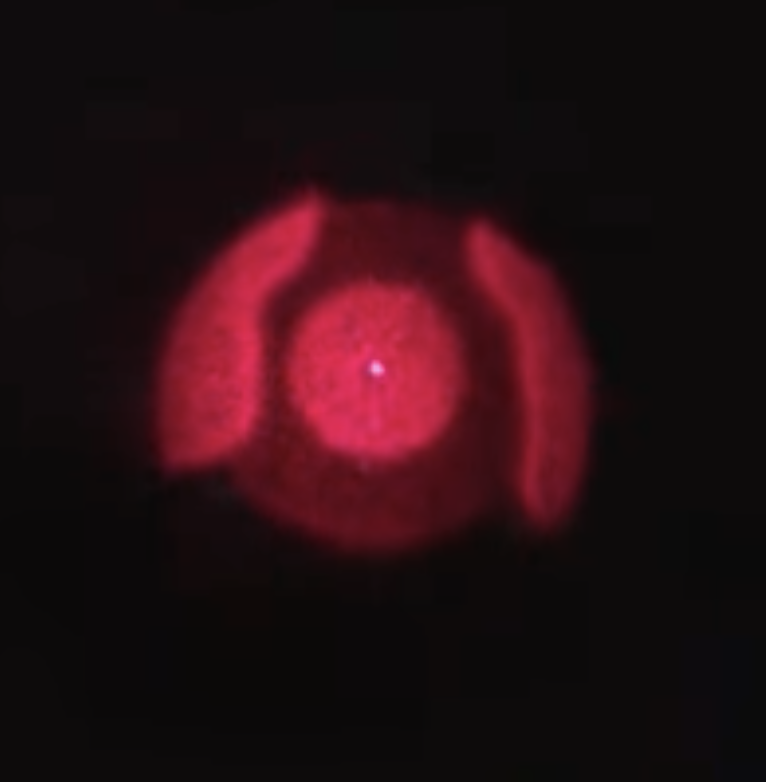
Below is an calculation of the intensity pattern at the focal distance of a zone plate from many spherical wave sources if the destructively interfering waves are not removed (left) and if they are removed.
Applications and Importance of Fresnel Zone Plates
Fresnel zone plates are used in various applications, particularly where traditional lenses are ineffective. Some key applications include:
X-ray Microscopy: Fresnel zone plates are used to focus X-rays, which have very short wavelengths and require special techniques for focusing. Traditional lenses are not effective for X-rays due to their low refractive indices.
Optical Systems: In optical systems, Fresnel zone plates can be used to create focal points without the need for bulky lenses. This is particularly useful in compact optical devices.
Holography: Fresnel zone plates are used in holography to create and reconstruct holograms. They help in manipulating the wavefronts to produce the desired holographic images.
Astronomy: In astronomy, Fresnel zone plates can be used in telescopes to focus light from distant stars and galaxies. They offer an alternative to traditional lenses and mirrors.